Entity Framework Extras Getting Started Entity Framework Extras
Introduction
As a web developer, if you have ever worked on enterprise applications using Entity Framework, many times you need to pass a group of records in stored procedure using user-defined table type. But Entity Framework does not support user-defined type by default. To support user-defined type in entity framework, we can use the EntityFrameworkExtras NuGet package.
What is the User Defined Table Type?
The User-Defined Table Types (UDTTs) and Table-Valued Parameters (TVPs) were first introduced in SQL Server 2008.
- Before SQL Server 2008, it was not possible to pass a table variable in a stored procedure as a parameter.
- Now we can pass a Table-Valued Parameter to send multiple rows of data to a stored procedure or a function without creating a temporary table or passing so many parameters.
What is EntityFrameworkExtras?
EntityFrameworkExtras provides some useful additions to Entity Framework such as executing Stored Procedures with User-Defined Table Types and Output Parameters.
NuGet Packages
- Entity Framework Core - https://www.nuget.org/packages/EntityFrameworkExtras.EFCore/
- Entity Framework 6 - https://www.nuget.org/packages/EntityFrameworkExtras.EF6/
- Entity Framework 5 - https://www.nuget.org/packages/EntityFrameworkExtras.EF5/
- Entity Framework 4 - https://www.nuget.org/packages/EntityFrameworkExtras/
Create Application
We are going to create a new Console application using Visual Studio 2019. The next step is to go to File -> New -> Project. In the Create a new project window, select Console in the Project type dropdown.
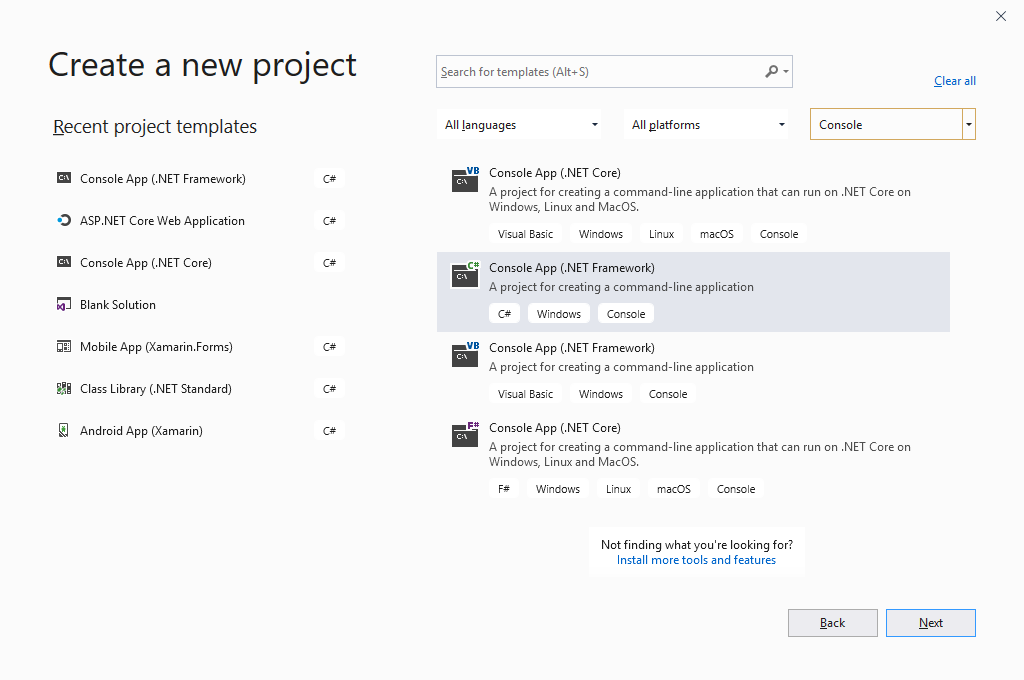
Select the Console App (.NET Framework) template and click the Next button.
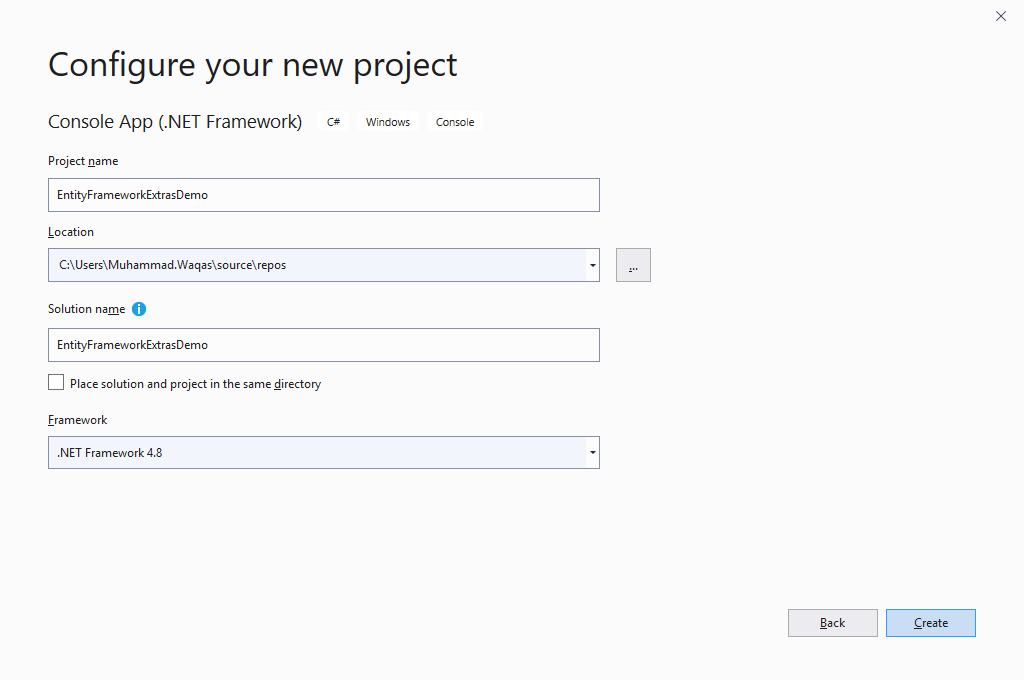
In the Configure your new project window, set the Project name to EntityFrameworkExtrasDemo, choose a suitable location for the project and you can also change the solution name, and click the Create button.
A Solution called EntityFrameworkExtrasDemo is created which contains a Console project EntityFrameworkExtrasDemo.
Install EntityFrameworkExtras
To install EntityFrameworkExtras, right-click on the EntityFrameworkExtrasDemo project in Solution Explorer, and select Manage NuGet Packages…,
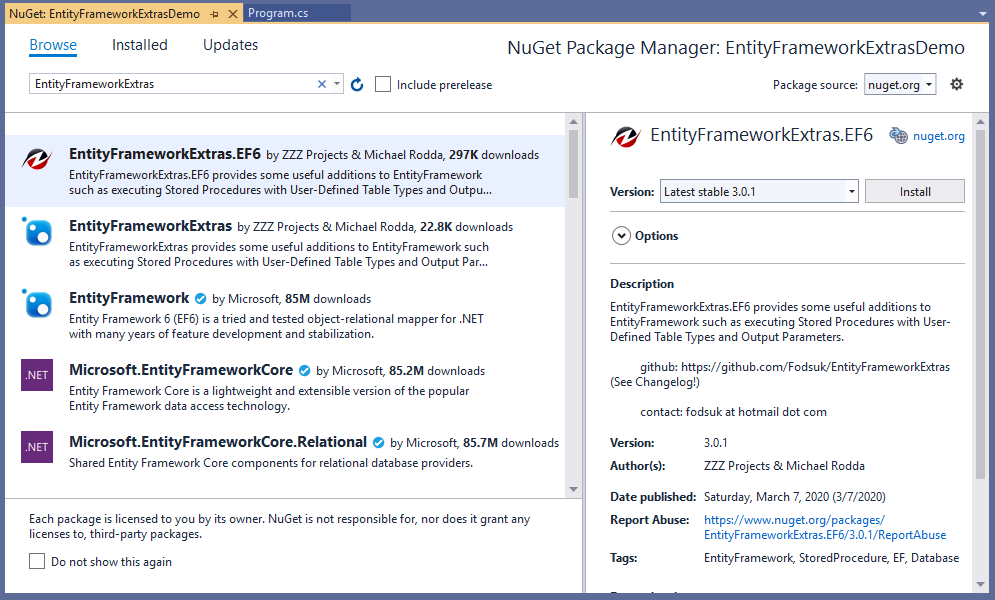
Search EntityFrameworkExtras and install EntityFrameworkExtras.EF6 NuGet package.
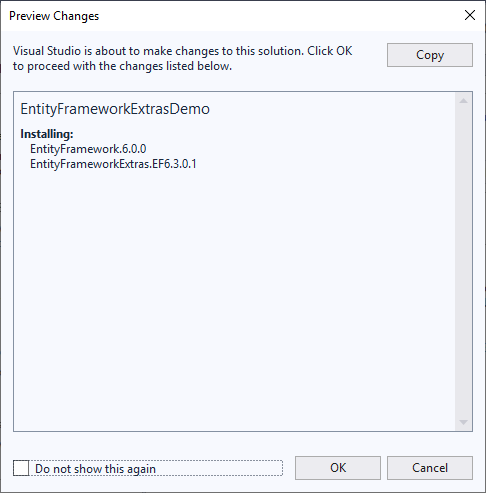 It will also install the **EntityFramework.6.0.0** NuGet Package.
It will also install the **EntityFramework.6.0.0** NuGet Package.
Create a Model
The model plays a significant part in the Entity Framework. It contains configurations, mapping properties, relationships, and defines which objects map to which tables.
Let’s create a new Customer class.
public class Customer { public int CustomerID { get; set; } public String Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } }
Create DbContext
If you have used Entity Framework before, you will know how to define a DbContext and the underlying Models that define a database schema. We have already created a simple model that has Customer and class, now let’s ensure that the Customer class is a part of the DbContext by defining a new context called EntityContext.
So first we will create a new class EntityContext.
public class EntityContext : DbContext { public EntityContext() : base("EntityContext") { } public DbSet<Customer> Customers { get; set; } }
Create User-defined Type
User-defined table type will allow you to declare table structure as a type in SQL Server, which may be used as a parameter for a stored procedure. Here is a sample code snippet to define a user-defined table type which allows us to pass the data table as a parameter.
CREATE TYPE [dbo].[CustomerUDT] AS TABLE (
[Name] NVARCHAR (MAX) NULL,
[Age] INT NULL);
The above user-defined table type has Name and Age columns.
Create Class for User-defined Table Type
Now create a class in your project that represents user-defined table type. Decorate class with [UserDefinedTableType("CustomerUDT")] attribute.
- Decorate class properties with [UserDefinedTableTypeColumn(1)] attribute.
- The name passed in the constructor must match with the name of the user-defined table type in the SQL server.
[UserDefinedTableType("CustomerUDT")] public class CustomerUDT { [UserDefinedTableTypeColumn(1)] public String Name { get; set; } [UserDefinedTableTypeColumn(2)] public int? Age { get; set; } }
Create Stored Procedure
Now create a stored procedure that uses the above-mentioned user-defined table type as a parameter. The below code snippet will define @UserDefinedTableParameter as a parameter, and it is a user-defined table type parameter.
CREATE PROCEDURE CustomerInsertWithUDT
@UserDefinedTableParameter CustomerUDT READONLY
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO Customers
(Name, Age)
SELECT Name, Age FROM @UserDefinedTableParameter
END
It will insert the list of customers information like Name and Age to the Customers table from the user-defined type which is passed as parameter.
Create Class for Stored Procedure
Let’s create another class in your project that will represent a stored procedure.
- Decorate class with [StoredProcedure("CustomerInsertWithUDT")] attribute.
- Decorate class properties with [StoredProcedureParameter(SqlDbType.Udt)] attribute.
- Mention type and name of parameter in [StoredProcedureParameter(SqlDbType.Udt)] constructor for each property.
[StoredProcedure("CustomerInsertWithUDT")] public class CustomerInsertWithUDT { [StoredProcedureParameter(SqlDbType.Udt)] public List<CustomerUDT> UserDefinedTableParameter { get; set; } }
Create Stored Procedure with Output Parameter
Now create a stored procedure with output parameter.
CREATE PROCEDURE GetOldestAge
@MaxAge INT OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
Select @MaxAge = MAX(Age) FROM Customers;
END
In this stored procedure, we created an output parameter named @MaxAge to store the age of the oldest customer.
Create Class for Stored Procedure with Output Parameter
Let’s create another class in your project that will represent a stored procedure with an output parameter.
[StoredProcedure("GetOldestAge")] public class GetOldestAge { [StoredProcedureParameter(SqlDbType.Int, Direction = ParameterDirection.Output)] public int MaxAge { get; set; } }
Now in this case, you can see that the MaxAge property is decorated with [StoredProcedureParameter(SqlDbType.Int, Direction = ParameterDirection.Output)]
Executing Stored Procedure
Now, let’s execute stored procedure using DbContext.
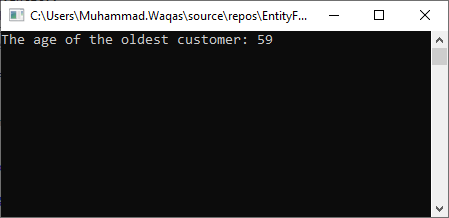
using (var context = new EntityContext()) { var proc = new CustomerInsertWithUDT(); proc.UserDefinedTableParameter = new List<CustomerUDT>() { new CustomerUDT() { Name = "Mark", Age = 32 }, new CustomerUDT() { Name = "Andy", Age = 59 }, new CustomerUDT() { Name = "Allan", Age = 23 }, new CustomerUDT() { Name = "John", Age = 41 } }; context.Database.ExecuteStoredProcedure<CustomerUDT>(proc); var proc1 = new GetOldestAge(); context.Database.ExecuteStoredProcedure(proc1); Console.WriteLine("The age of the oldest customer: {0}", proc1.MaxAge); }
Now let’s run your application and you will see the age of the oldest customer.
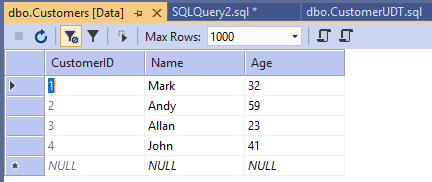
 Now if you open the Customers table, you will see all the customers are inserted using the stored procedure with user-defined type.
Now if you open the Customers table, you will see all the customers are inserted using the stored procedure with user-defined type.